Dr Thomas Edwards
- Position
- Visiting member
- Areas of expertise
- structural biology; protein-protein interactions; RNA virus; crystallography; RNA binding proteins
- tedwards@ularkin.org
- Faculty profile link
- https://www.ularkin.org/team-member/thomas-edwards/#research
Introduction
We use Structural Molecular Biology (mainly X-ray crystallography, but including NMR and EM) to study protein-protein and protein-RNA interactions in Developmental & Cellular Biology, Microbiology, and Cancer.
Current major projects
- RBPs & N proteins from -ve sense RNA viruses
- Protein-protein interactions and their inhibition
- RNA binding proteins in developmental control
- Affimers and conformational selection
Detailed research programme
Perturbation of protein-protein interactions (PoPPI)
An EPSRC funded programme grant in collaboration with the University of Bristol, Northern Institute for Cancer Research (Newcastle University), AstraZeneca and Domainex.
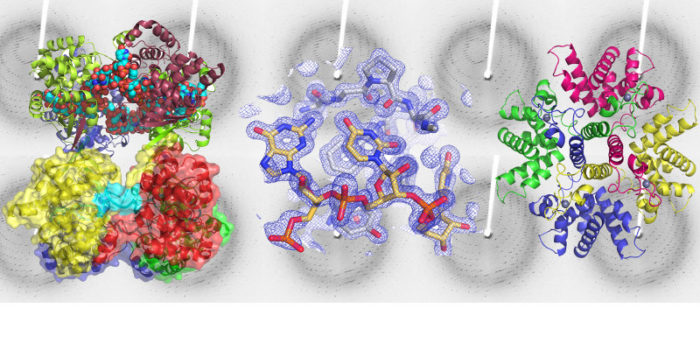
https://poppi.website/. The figure shows the HIF1:p300 interaction that we are trying to inhibit in cancer cells to prevent vascularisation in solid tumours.
RBPs & N proteins from -ve sense RNA viruses.
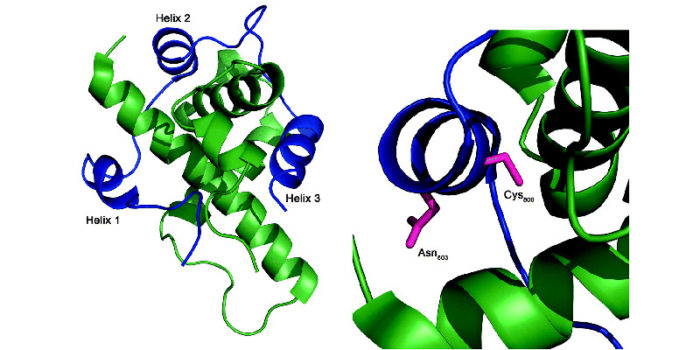
Structural biology of RNA binding proteins from negative sense RNA viruses, including the M2-1 protein from Respiratory Syncytial Virus (shown below in complex with the binding peptide from the P protein), and Nucleocapsid (aka nucleoprotine, N or NP) proteins from bunyaviruses.
Affimers and conformational selection
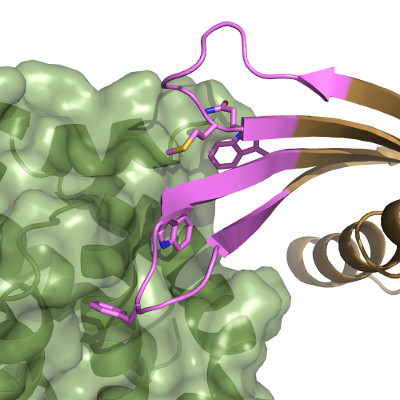
Crystal structures of selective Affimers in complex with their target proteins has revealed a conformational selection that traps the target protein into what could be a desirable conformation. The figure shows an MCL-1 selective Affimer in complex with MCL-1, a target for anti-cancer therapeutics.
RNA binding proteins in developmental control. The control of RNA translation and localisation can be critical in developmental biology Structural biology reveals the mechanism of binding and sequence selectivity, for instance the structure of Pumilio shown in the figure.